What does the human brain look like?
There are three main parts of the brain: the cerebrum, the cerebellum and the brain stem. Each part is in charge of different things. Parts of the brain work closely together and send messages to each other and to other parts of the body to control everything we do, feel and think.
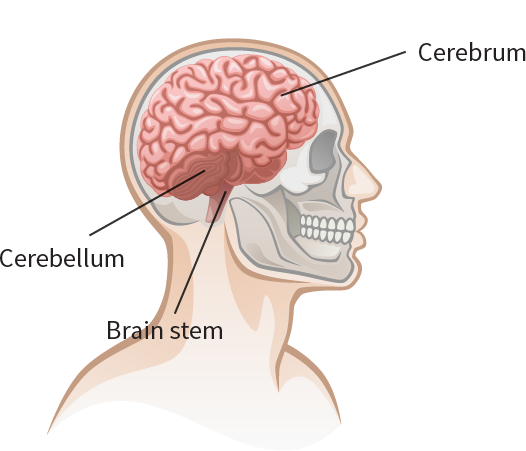
The brain has a texture like firm jelly. In most cases, a minor hit to the head does not cause any lasting problems. This is because the brain is well protected by shock-absorbing liquid called cerebro spinal fluid, layers of tissue called meninges and the hard part of the head, called the skull.
The brain is also made up of chemicals and nerve cells that send messages to different parts of the brain and body. The brain uses these messages to do important things such as:
- Control the way our body moves
- How we think, make decisions, learn and remember
- How we speak
- Our personality and behaviour
- Our vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch
- Things we don’t think about, such as breathing, heart rate, body temperature and blood pressure
What happens to the brain when it is injured?
A mild traumatic brain injury/concussion is caused by a blow or jolt to the head. Concussions can also happen from a blow or jolt to the body that causes the head to move quickly back and forth. This can cause the brain to bounce around inside the skull.
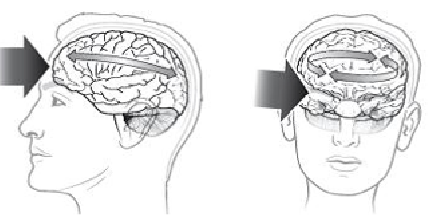
This sudden movement can twist and stretch the cells and nerves in the brain or change how chemicals in the brain work for a short time. When this happens it can change the way the brain is able to send messages to the brain and body. This is why after a concussion, you might think, act, move or feel differently for a while.
If the brain moves hard enough inside the skull it can sometimes hurt the tissue that covers and protects the brain. The brain can then bang against the ridges that are on the inside of the skull. Depending where the brain hits will determine what parts of the brain are affected. Sometimes there is bleeding that can cause the brain to bruise. Just like a bruise on your leg or arm, this will heal.
Sometimes a doctor will order brain imaging tests like a computed tomography (CT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to show pictures of the brain more clearly. In many concussions, brain imaging is normal and does not show changes in the brain.
Every brain injury is different. Talk to your doctor or health care provider if you have questions about your diagnosis or injury.






